Content
Understanding the health risks that come from being overweight or obese can be challenging. For many people who are overweight, life seems to slow down, with fewer activities being possible or enjoyable. At the same time, the body begins to struggle, and disease can develop. Recognizing the risks of being overweight and obese is critical to taking the next step in treatment.
One of the most important aspects of this process is recognizing that you are not alone when it comes to being obese or overweight.
Facts About Obesity and Overweight Statistics
A person who is overweight is at a weight that is higher than considered acceptable from a health perspective. The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases shares some interesting statistics about the US population.

- 7% of people are overweight. That’s 1 in 3 adults in the US.
- 4% of people have obesity. That’s 2 in 5 adults in the US.
- 2% of people have severe obesity. That’s 1 in 11 adults in the US.
Children are also impacted in the same way. In the US, children between the ages of 2 and 19 fall into these areas:
- 1% of children are overweight. That’s 1 in 6 children.
- 3% of children have obesity. That’s 1 in 5 children.
- 1% of children have severe obesity. That’s 1 in 16 children.
Gender-Related Factors
The same organization provides insight into the percentage of men and women who are obese or overweight.
- 1% of men are overweight, and 27.5% of women are overweight.
- 5% of women have severe obesity, and 6.9% of men have severe obesity.
Age Factors Related to Obesity and Overweight Concerns

There is a significant difference in obesity and overweight health conditions related to age. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides some specific areas of consideration here:
- About 41.9% of adults 20 years of age or older have obesity.
- 6% of adults under the age of 20 are overweight.
- 2% of children between the ages of 12 and 19 have obesity.
- 7% of children between the ages of 6 and 11 have obesity.
- 7% of children between the ages of 2 and 5 have obesity.
Seniors are specifically at risk for health complications due to obesity and being overweight, and the number of people with these conditions is significant. The Health Policy Institute shares that 15 million people over the age of 51 are obese. That is about 1 in 4 older adults. It is one of the leading factors in the top 10 causes of death in these individuals, including type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease, strokes, and cancer.
One of the most interesting factors here is that disability rates are higher among those who are obese. That means that those who have trouble with eating, dressing, and bathing are more likely to have obesity. These individuals have a significantly lower quality of life than those who are not obese. Activities like socializing, shopping, and outdoor experiences are far more limited in those who are overweight and obese at an older age.
Obesity and Being Overweight Related to Ethnicity
Another way to consider the impact of obesity and being overweight is to consider ethnic makeup. The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases provides data on how ethnicity plays a role.
In obesity, the following statistics apply:
- 6% of non-Hispanic Black adults suffer from obesity. That’s nearly 1 in 2 people.
- 8% of Hispanic adults suffer from obesity. That’s 1 in 8 people.
- 2% of non-Hispanic white adults suffer from obesity. That’s 2 in 5 people.
- 4% of non-Hispanic Asian adults suffer from obesity. That’s 1 in 6 people.
In severe obesity, the following statistics apply:
- 8% of non-Hispanic Black adults suffer from severe obesity. That’s 1 in 8 people.
- 3% of non-Hispanic white adults suffer severe obesity. That’s 1 in 11 people.
- 2% of non-Hispanic Asian adults suffer from obesity. That’s 1 in 50 people.
- 9% of Hispanic adults suffer from severe obesity. That’s 1 in 13.
How Being Overweight or Obese Is Defined
The statistics above refer to the Body Mass Index (BMI) method to estimate obesity and overweight factors. BMI is a type of tool that is applied to both children and adults. It considers the amount of fat present in the body compared to overall height. Researchers know that a higher percentage of body fact can lead to a much higher risk of health complications and early death.
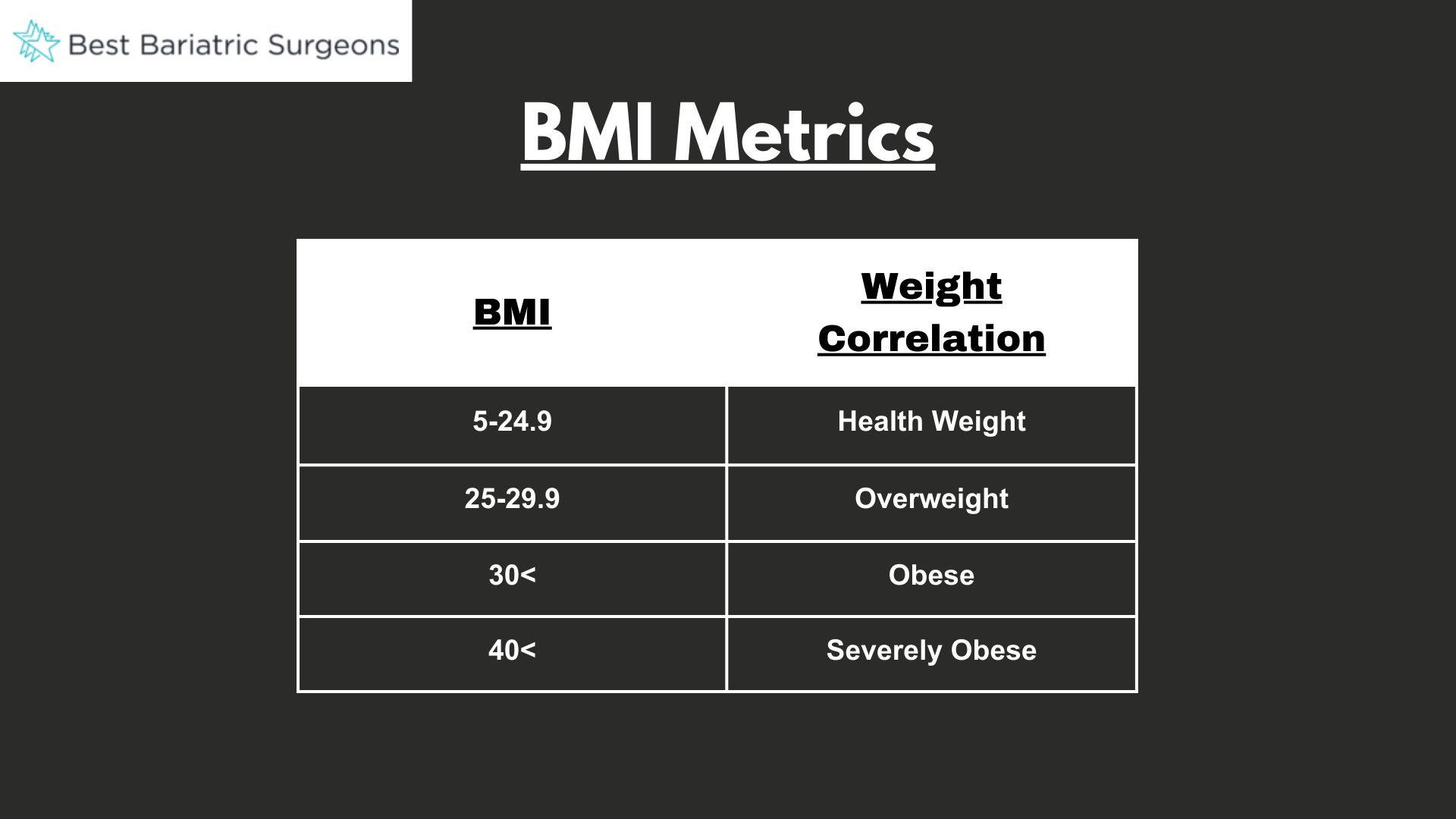
The BMI calculations include the following:
- 5 to 24.9: Normal BMI or a healthy weight
- 25 to 29.9: Overweight BMI
- 30 or higher: Obesity, including severe obesity
- 40 or higher: Severe obesity
A person can use the following tool from the CDC to help in the calculation of obesity. This calculate allows for a person to input their height and weight to determine what their BMI is. This tool, often used by doctors, can be a starting point to recognizing the risk factors to health concerns.
Research indicates that a person with a lower BMI is less likely to develop weight-related health complications. Yet, BMI can be somewhat misleading in those who have built a significant amount of muscle. In all cases, it is a tool to provide more insight into overall health.